Breaking down projects into smaller managable components means that the project is more manageable, easy to update and test, code reuse. You normally have a root project and then sub-projects within that root project, these sub-projects could have dependencies on other sub-projects.
A example multi-project is below, again I am only covering the Gradle parts
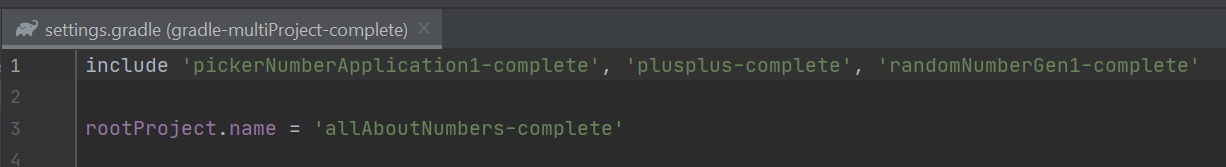
We start with the setting file as its mandatory when using a multi-project projects, it is used to include the sub-projects, we use the include method to include the sub-projects. We can also name the project using the rootProject.name property
When then can start on the root project build.grade file, we use the subprojects block to provide configuration to all the sub-projects. Once created thats pretty much it as you can see it's much less work than Maven.
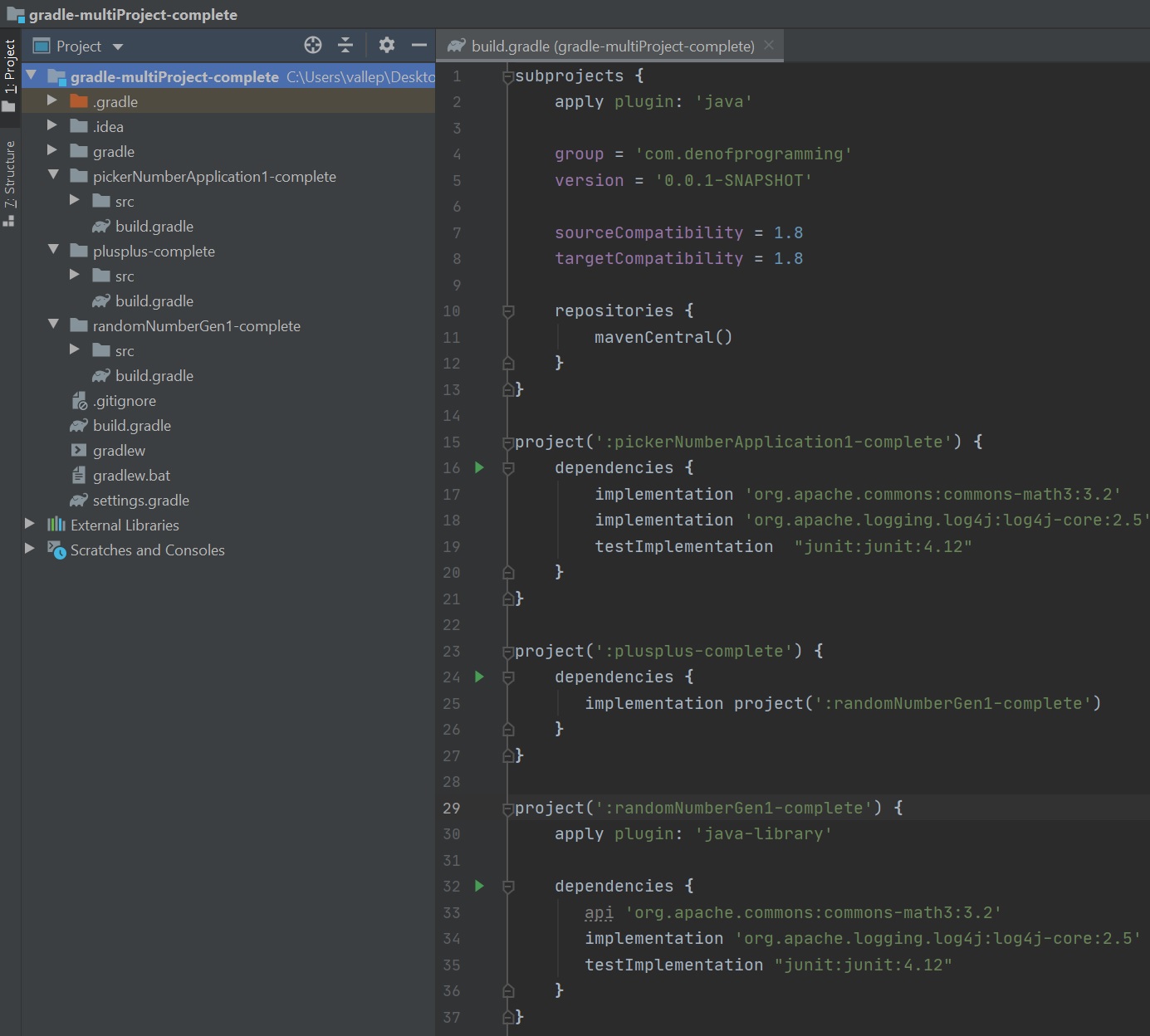
| all sub-projects will inherit the configuration in the subprojects block | subprojects {
apply plugin: 'java' // use the apply to apply to all sub-projects
group = 'com.denofprogramming'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
targetCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
// dependencies {} // add common dependencies that all sub-projects require
} |
| Use the project object for each of the sub-projects, use a path to indicate where the sub-project resides, each sub-project needs to be included. Now you can confiure each sub-project in the build.gradle file. | project(':pickerNumberApplication1-complete') {
dependencies {
implementation 'org.apache.commons:commons-math3:3.2'
implementation 'org.apache.logging.log4j:log4j-core:2.5'
testImplementation "junit:junit:4.12"
}
}
project(':plusplus-complete') {
dependencies {
implementation project(':randomNumberGen1-complete') // you can have an internal dependency
}
}
project(':randomNumberGen1-complete') {
apply plugin: 'java-library' // you can apply specific plugins in a sub-project
// we will use the api scope to import a library below
dependencies {
api 'org.apache.commons:commons-math3:3.2' // api is used to declare dependencies which are
// exported by the library API
implementation 'org.apache.logging.log4j:log4j-core:2.5'
testImplementation "junit:junit:4.12"
}
} |
Other useful tips for multi-projects
Below are some useful plugins that yopu can include into your project, there are many others best see the Grade documentation for the must up todate plugins and examples on how to configure them.
| settings.gradle - use for for renaming sub-projects build.grade file to something more meaningful | rootProject.children.each { subproject ->
subproject.buildFileName = "${subproject.name}.gradle"
} |
| build.grade - create your own tasks that have dependencies | task delpoy(dependsOn: ':academy-web:deployToTomcat') {
doLast{
println ">>>Deploying artifacts"
}
} |
| build.grade - spotbus is a plugin to find bugs in Java programs, it generates reports | spotbugs {
toolVersion = "4.0.4"
}
dependencies {
spotbugsPlugins 'com.h3xstream.findsecbugs:findsecbugs-plugin:1.10.1'
} |
| build.grade - pmd is a source code analyser, to find things like unused variables, empty try-catch blocks, etc. | pmd {
ignoreFailures = true
pmdTest.enabled= false
ruleSets = [
'java-basic',
'java-braces',
'java-clone',
'java-codesize',
'java-comments',
'java-controversial',
'java-coupling',
'java-design',
'java-empty',
'java-finalizers',
'java-imports',
'java-optimizations',
'java-strictexception',
'java-strings',
'java-typeresolution',
'java-unnecessary',
'java-unusedcode'
]
} |