The topics for this section are the following:
- Describe Java Technology and the Java development environment
- Identify key features of the Java language
Describe Java Technology and the Java Development Environment
A Java Environment consists of the following
- An environment (JDK consists of development tools, compiler, debugger, class inspector and document generator)
- The language
- Java Application Programming Interface (API)
- Various Classes
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE)
Java has to go through 5 phases into order to execute a java program
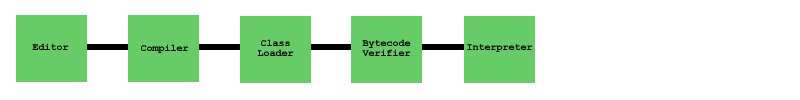
| Editor | You create Java source code with a text editor such as vi (unix) or notepad (windows), the file will have a .java extension. you can use a IDE (integrated development Environment) such as JCreator, JEdit or eclipse. |
| Compiler | You use the command javac to compile the source code, this checks the syntax and translates the source code into bytecode, the language understood by the java virtual interpreter. A file with a .class extension is created. |
| Class Load | This phase loads the .class file into memory (the file can either be on disk or copied over a network) The .class file can be either a application program (run on your computer) or a applet (run within a web browser) |
| Bytecode Verifier | This phase checks that the bytecode meets Java's security restrictions, it enforces very strict rules to protect data on your computer. |
| Interpreter (Execute) | The last phase executes the bytecode one byte at a time using the JRE (Java Runtime Environment), thus performing the action you asked when to created the source code. |
Identify key features of the Java language
For the exam you need to to have a understanding of the features of the Java programming language
Object Oriented - In Java, nearly everything is an Object (Java supports primitive data types). Java can be easily extended since it is based on the Object model.
Statically Typed - All variables have to be declared with a data type before using them
Platform Independent/Portability - When Java is compiled, it is not compiled into platform specific machine, rather into platform-independent byte code (Write Once and Run Anywhere - WORA). This byte code is distributed over the web and interpreted by the Virtual Machine (JVM) on whichever platform it is being run on.
Interpreted - Java byte code is translated on the fly to native machine instructions.
Simple to Learn - Java is designed to be easy to learn as you don't have to pre-allocate memory (use pointers). It is now the default language to learn in universities
Memory Management - Java uses a garabge collector to reclaim any memory that is not required
Secure - With Java's secure feature it enables to develop virus-free, tamper-free systems. Authentication techniques are based on public-key encryption.
Robust - Java makes an effort to eliminate error-prone situations by emphasizing mainly on compile time error and runtime checking.
Multithreaded - With Java's multithreaded feature it is possible to write programs that can perform many tasks simultaneously.
High Performance - With the use of Just-In-Time compilers, Java enables high performance..