Heaps and Sets
Heaps are a special type of complete binary tree, you have two types min/max heap (heap property), max heap is that every parent is geater than or equal to its children or min heap every parent is less than or equal to its children. The Maximum or Minimum value will always be at the root of the tree as you can see in the below diagrams, plus both examples are complete trees.
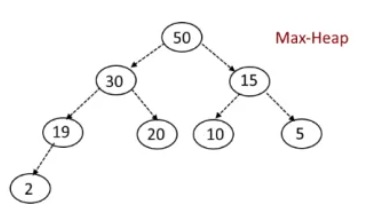 |
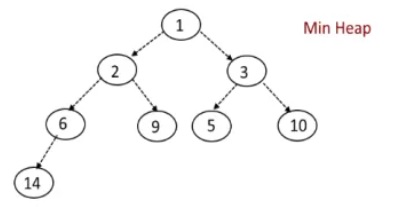 |
An example of an heap which also includes a sort
| Max Heap | package uk.co.datadisk.heap;
public class MaxHeap {
private int[] heap;
private int size;
public MaxHeap(int capacity) {
heap = new int[capacity];
}
public void insert(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Heap is full");
}
heap[size] = value;
fixHeapAbove(size);
size++;
}
public int delete(int index) {
if (isEmpty()){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Heap is empty");
}
int parent = getParent(index);
int deletedValue = heap[index];
heap[index] = heap[size - 1];
if(index == 0 || heap[index] < heap[parent]) {
fixHeapBelow(index, size - 1);
} else {
fixHeapAbove(index);
}
size--;
return deletedValue;
}
public void sort() {
// Once a heap is sorted then it's NO LONGER A HEAP
int lastHeapIndex = size - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < lastHeapIndex; i++) {
int tmp = heap[0];
heap[0] = heap[lastHeapIndex - i];
heap[lastHeapIndex - i] = tmp;
fixHeapBelow(0, lastHeapIndex - i - 1);
}
}
private void fixHeapAbove(int index) {
int newValue = heap[index];
while ( index > 0 && newValue > heap[getParent(index)] ) {
heap[index] = heap[getParent(index)];
index = getParent(index);
}
heap[index] = newValue;
}
private void fixHeapBelow(int index, int lastHeapIndex){
int childToSwap;
while(index <= lastHeapIndex) {
int leftChild = getChild(index, true);
int rightChild = getChild(index, false);
if(leftChild <= lastHeapIndex){
if(rightChild > lastHeapIndex){
childToSwap = leftChild;
} else {
childToSwap = (heap[leftChild] > heap[rightChild] ? leftChild : rightChild);
}
if (heap[index] < heap[childToSwap]) {
int tmp = heap[index];
heap[index] = heap[childToSwap];
heap[childToSwap] = tmp;
} else {
break;
}
index = childToSwap;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == heap.length;
}
public void printHeap() {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print(heap[i]);
System.out.print(", ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public int getParent(int index) {
return (index - 1) / 2;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public int getChild(int index, boolean left) {
return 2 * index + (left ? 1 : 2);
}
public int peek() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Heap is empty");
}
return heap[0];
}
} |
| Main Max Heap | package uk.co.datadisk.heap;
public class Main_MaxHeap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Only use heaps for MIN and MAX values, use something else for random deletes, etc
MaxHeap maxHeap = new MaxHeap(10);
maxHeap.insert(80);
maxHeap.insert(75);
maxHeap.insert(60);
maxHeap.insert(68);
maxHeap.insert(55);
maxHeap.insert(40);
maxHeap.insert(52);
maxHeap.insert(67);
System.out.println("Peek is " + maxHeap.peek());
maxHeap.printHeap();
//maxHeap.delete(1);
//maxHeap.printHeap();
//maxHeap.delete(5);
//maxHeap.printHeap();
//maxHeap.delete(0);
//System.out.println("Peek is " + maxHeap.peek());
//maxHeap.printHeap();
System.out.println("----------------------");
maxHeap.printHeap();
maxHeap.sort();
maxHeap.printHeap();
}
} |
PriorityQueue is based on a priority heap, they use natural ordering, the head of the queue is the least element (min heap), you can use a comparator to change the ordering.
| PriorityQueue | package uk.co.datadisk.heap;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Main_PriorityQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// REMINDER: its a MIN heap
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add(25);
pq.add(-22);
pq.add(1343);
pq.add(54);
pq.add(0);
pq.add(-3492);
pq.add(429);
System.out.println(pq.peek());
System.out.println(pq.remove());
System.out.println(pq.peek());
System.out.println(pq.poll());
System.out.println(pq.peek());
pq.add(-1);
System.out.println("--------------------");
for (Object o : pq.toArray()) {
System.out.println( (o));
}
}
} |