Puppet Cheatsheet
This is a quick and dirty cheatsheet on puppet. first some puppet terms
| Puppet Master | The Puppet server that controls the flow and has the authority, SSL is used for communication with Nodes |
| Puppet Node | A server with the puppet agent installed and connected to a puppet master. |
| Catalog | A catalog is a document that describes the desired state for each resource that Puppet manages on a node. A Puppet master typically compiles a catalog from manifests of Puppet code. The catalog consists of the following agent provided data, external data and puppet manifests. |
| Facts | Puppet collects system information, called facts, by using the Facter tool. The facts are assigned as values to variables (key/value pairs) that you can use anywhere in your manifests. |
| Report | The actions and infrastructure supplied by a catalog during a puppet run. |
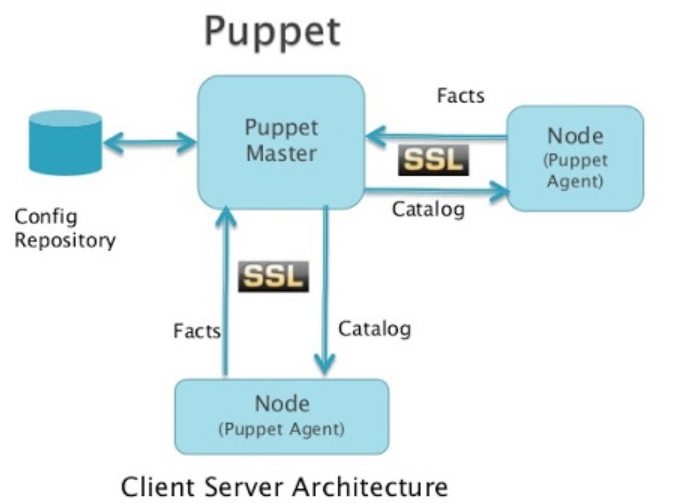
Below are some of the commonly used puppet commands, see documentation for all commands
| Install (this may change) | rpm -ivh https://yum.puppetlabs.com/puppet5/puppet5-release-el-7.noarch.rpm yum install puppetserver -y yum install puppet-agent -y |
| Files and Directories | puppet config print reportdir ## add external facts (use key/value pairs) /etc/facter/facts.d vi facts.txt # example owner=Paul Valle |
| Agents Certificate and Connection test | ## generate agents certifcate (make sure server is configured in puppet.conf file) puppet agent --verbose --no-daemonize --onetime ## get the agents cert (look for the plus sign (+) which means they have been signed) puppet cert list # certs waiting to be signed puppet cert list --all # everything ## make sure you sign the cert for the clients (run on master) puppet cert sign <hostname> puppet cert sign --all ## test connection from puppet master puppet agent --test --server <puppet master> ## remove a specific agents certificate puppet cert clean <cert> ## remove all certs and start again (https://puppet.com/docs/puppet/5.5/ssl_regenerate_certificates.html) rm -rf /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl/ # from server or agent ## automatic agent certificate signing puppet.conf [master]: autosign = true cd /var/lib/puppet/ vi autosign.conf cat autosign.conf *.packt.com |
| Version | puppet --version puppet master --version puppet agent --version |
| Enable/Disable puppet or agent | ## enable and start service puppet master systemctl enable puppetserver systemctl start puppetserver ## enable and start service puppet agent systemctl enable puppet systemctl start puppet ## disable and enable puppet agent puppet agent --disable puppet agent --enable |
| Display/Change config | ## show master config puppet master --configprint all ## change configuration via commandline (or us vi) puppet config set runinterval 5m --section agent |
| Debug, Stats and Validate puppet file | ## statistics - this may hang?? puppet apply --summarize ## debug and test run puppet apply --debug puppet apply --noop ## validate puppet file puppet parser validate <pp file> |
| Getting help | puppet master --genconfig /var/log/messages or /var/log/syslog (agent messages) puppet resource --types ## list all resource types puppet describe --list ## describe resource types puppet describe <type - see above command> ## detail help on type puppet resource service ## list resource type service (like man page) |
| Check server information (facter) | facter domain facter hostname facter fqdn facter system_uptime.hours facter ssh.dsa.fingerprints.sha1 facter [-p|-y|-j] facter -p <name> |
| Test mode | puppet -t --noop |
| Apply Manifest | ## apply a puppet manifest file, also update basemodulepath in puppet.conf if not deault location puppet apply <manifest file> [--modulepath=/puppet/modules/] ## apply manifest file from client, used for one time only updates puppet agent --verbose --no-daemonize --onetime ## check what manifest file will be used for your environment (master) puppet config print manifest --section master --environment production |
| File Bucket | puppet filebucket -l list -b /opt/puppetlabs/puppet/cache/clientbucket |
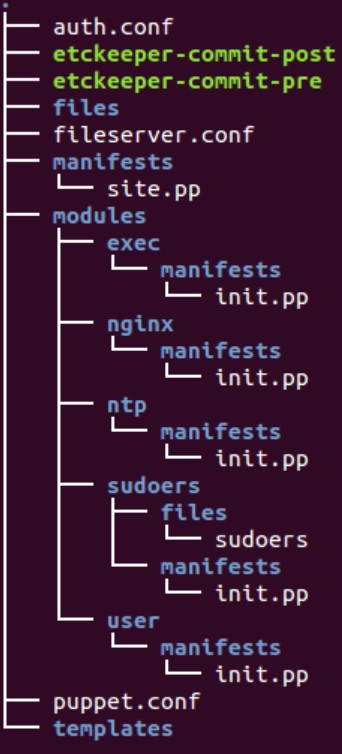
Below is an example directory structure, I have also includes some examples of a node file and of a module/class file.
| Module commands | puppet module list puppet module install <name> puppet module uninstall <name> puppet module upgrade <name> puppet module search <name> |
| Example Puppet file | NODE File
------------------------------------------------------------------------
node 'gbvmub01' {
include nginx
include ssh
## you can move this into another pp file if you so wish
class { 'nginx::test':
fname1 => 'Paul',
lname1 => 'Valle',
}
## there are a number of conitional operators: == != >= <=
## for strings there are: in =~ !~ ?
## boolean: and or
## arithmetic: + / * - <<
## capture: ${0} ${1}...
## is a good idea to call classes/modules using code, using code to
## determine what to call
if $::processorcount >= 16 {
notify { 'Heavy Server': }
## include heavy_modules_or_classes
} elsif $::processorcount >= 4 {
notify { 'Meduim Server': }
## include meduim_modules_or_classes
} else {
notify { 'Light Server': }
## include light_modules_or_classes
}
## you can use case statements
case $::operatingsystem {
'Ubuntu', Debian: { notify { 'Ubuntu or Debian': } }
'RedHat': { notify { 'RedHat': } }
default : { notify { 'default': } }
}
}
node 'gbvmub02' {
include nginx
include ssh
}
node 'node1.packt.com' {
user {'paul.valle':
ensure => 'present',
comment => 'Paul Valle Account',
home => '/home/pvalle',
shell => '/bin/bash',
uid => '1001',
}
file {'/tmp/sshd_config':
ensure => 'present',
source => '/etc/ssh/sshd_config',
}
file_line {'tcp-forwarding':
path => '/tmp/sshd_config',
line => 'AllowTcpForwarding yes',
require => File['/tmp/sshd_config'],
}
} |
| Module/Class file | MODULE/CLASS File
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Manage nginx webserver
class nginx {
package { 'nginx':
ensure => installed,
}
service { 'nginx':
require => Package['nginx'],
ensure => running,
enable => true,
}
file { '/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default':
source => 'puppet:///modules/nginx/cat-pictures2.conf',
notify => Service['nginx'],
}
user { 'art':
ensure => present,
comment => 'Art Vandelay',
home => '/home/art',
managehome => true,
}
ssh_authorized_key { 'art_ssh':
user => 'art',
type => 'rsa',
key => 'AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EA...',
}
exec { 'Run my arbitrary command':
command => '/bin/echo I ran this command on `/bin/date` >/tmp/command.output.txt',
path => ['/bin', '/usr/bin'],
}
exec { 'Download public key for John':
cwd => '/tmp',
command => '/usr/bin/wget http://bitfieldconsulting.com/files/john.pub',
creates => '/tmp/john.pub',
}
## it will blow away cron to create the below
cron { 'Back up cat-pictures':
command => '/usr/bin/rsync -az /var/www/cat-pictures/ /catpictures-backup/',
hour => '13',
minute => '40',
}
$site_name = 'cat-pictures'
$site_domain = 'cat-pictures.com'
file { '/tmp/cat-pictures.conf':
content => template('nginx/vhost.conf.erb'),
notify => Service['nginx'],
}
## inline templates, the calcuation is ruby code
file { '/tmp/the_answer.txt':
content => inline_template("What do you get if you multiply six by nine? <%= 6 * 7 %>.\n")
}
## here we use a inline template and facter @ipaddress
file { '/tmp/the_answer2.txt':
content => inline_template("My IP Address is: <%= @ipaddress %>.\n")
}
## some define jobs examples, the job name can be anything
define script_job() {
file { "/tmp/${name}":
source => "puppet:///modules/scripts/${name}",
mode => '0755',
}
}
script_job { 'hello_world.txt': }
## passing parameters to a script, notice a default value for location
define script_job1($fname, $lname, $location = 'London') {
file { "/tmp/$name.txt":
content => inline_template("Your name is $fname $lname and you are from $location\n")
}
}
script_job1 { 'the_answer3':
fname => 'Paul',
lname => 'Valle',
}
## You can also call classes from here as well
#class { 'nginx::test':
# fname1 => 'Paul',
# lname1 => 'Valle',
#}
## You can use code anywhere
#if $::processorcount >= 16 {
# notify { 'Heavy Server': }
#} elsif $::processorcount >= 4 {
# notify { 'Meduim Server': }
#} else {
# notify { 'Light Server': }
#}
} |