Once Python has been installed it comes with a large rich standard library, this means you can perform various tasks without adding additional 3rd party libraries. These standard libraries are already imported so to speak and can be freely used, in the table below I list the most commonly used modules and highlight the service type, there are thousands of moudules in the wild so use google to see if something as already been creaetd to help you solve your problem.
| String modules | |
| string | Compare with string constants such as digits |
| re | regular expressions |
| struct | read and write structured data to/from files |
| Data Types modules | |
| datetime, calendar | Date, time and calendar operations |
| collections | high performance data types |
| enum | enumeration classes that bind symbolic names to constant values |
| sched | Eevent scheduler |
| queue | synchronised queue class |
| Numeric and Mathematical modules | |
| numbers | Numeric abstract base classes |
| math, cmath | complex numbers and mathimatical functions |
| decimal | fixed-point and floating-point arithmetic |
| random | Generator random numbers |
| System modules | |
| os | Operating system information |
| io | Use streams for IO |
| time | Time access and conversion |
| logging | Logging module for Python |
| curses | Terminal GUI |
| platform | Get platform information |
| threading | High-level threading interface |
| multiprocessing | Process based threading interface |
| Internet protocol modules | |
| socket, ssl | Network interface |
| Email handling | |
| json | JSON encoder and decoder |
| http.server | HTTP servers |
| Devlopment and Debugging modules | |
| pydoc | Document generator |
| doctest | Test interactive Python examples |
| unittest | Unit testing framework |
| pdb | Python debugger |
| trace | Trace or track Python statement execution |
| inspect | Inspect live objects |
As I mentioned above there are many thousands of modules out in the wild, many of which can be downloaded or viewed at pypi, however there is a tool that you can use that will install the module into your current Python installation. Python offers pip, it is a module installer that also installs any dependencies and the module that you wanted, and it can be used on various operating systems.
To install pip (if not already installed)
| Installing pip | ## Download get-pip.py python get-pip.py pip -V # get version |
| Upgrading pip | python -m pip install --upgrade pip |
To install modules into main Python system instance use the below commands, I will discuss how to install module into your own directory and not in the main Python instance, also you can remove or list modules
| Installing a module | pip install camelcase pip install 'camelcase>=0.2' # specific version pip install 'camelcase>=0.2,<0.5' # a specific version range |
| Remove a module | pip uninstall camelcase pip uninstall 'camelcase=0.2' # remove specific version of module |
| List all installed modules | pip list |
Python by default install modules in the main Python installation area, there are times when you just want to maybe test somehting an don't want to install a module into the main area, the is called virtual environment, its a self contained directory structure tht contains the modules that you need, and thus they will not conflict with an existing modules installed in the main area. To create a virtual environment firstly you create the environment, which creates a directory structure named as specified this is were the modules will live and secondly you need to run a script to source the virtual environment and then you use pip as normal.
| Create virtual environment | python -m venv test-env |
| Source the new enviroment | test-env\Scripts\activate.bat |
| Install modules | pip install camelcase |
Below are some screenshots of the process using windows, notice that the prompt changes when you source the virtual enviroment
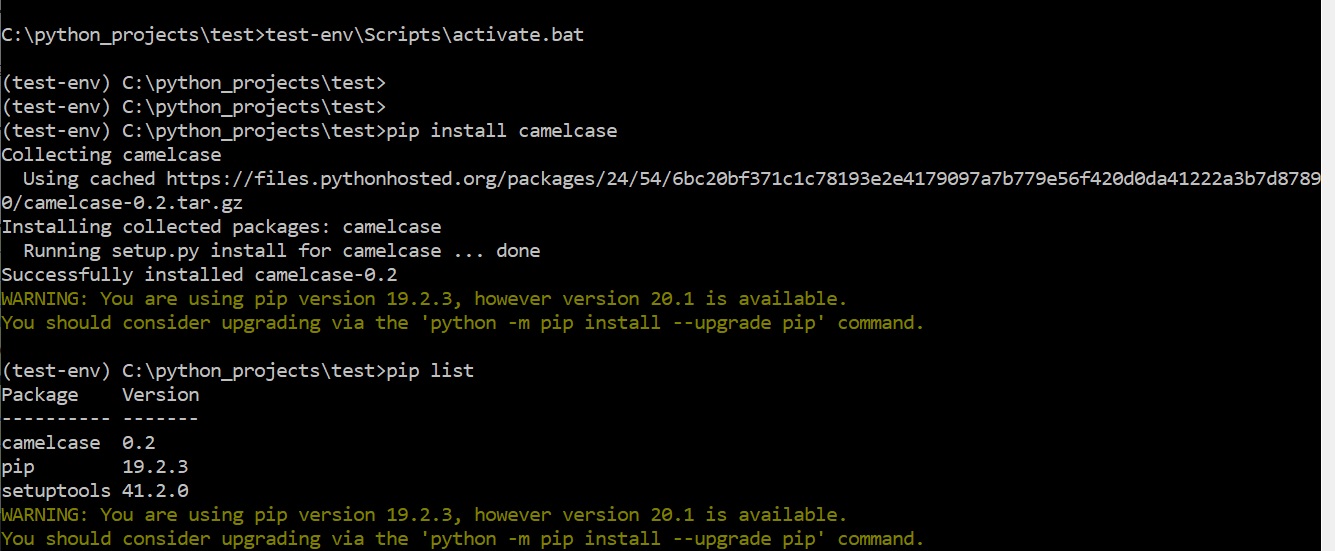
Notice that the main Python area does not have camelcase installed
