Introduction
In the old days data centers were full of physical servers doing nothing or at most running at only 10% capacity, this was a waste of money (power, cooling, support contracts, etc) and space. Companies are always looking to reduce the overall costs and that is were virtualization comes in.
Virtualization has been around since the 1970's, it was not until the late 1990 that virtualization became a hot topic once again, in 1999 a company called VMware released VMware Workstation which was designed to run multiple Operating Systems at the same time on a desktop PC. In 2001 VMware release two servers versions called VMware GSX server (requires a host O/S to run) this was later renamed VMware server and VMware ESX server this had it's own VMKernel (known as the hypervisor) and was run directly on the hardware, also a new filesystem was created called VMware Machine File System (VMFS). Since the first release we have had many releases the lastest at this time is VMWare vSphere 7.0
VMware ESXi server has seen many changes over the years and the latest versions includes support for the following, I will be going into much more depth with the below topics.
- High Availability (Clustering)
- Virtual Machine VMotion
- Storage VMotion
- VSAN Storage
- Fault Tolerance
- Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS)
- Distributed Power Management (DPM)
- Data Recovery
- vCenter (Managament)
- vSphere with Kubernetes
- NSX-T Networking
Going back to my first paragraph, virtualizing many servers reduces costs, administration and space and as most companies are now trying to reflect a green image, virtualizing whole environments (including Production environments) seem to be the way things are going.
So what is virtualization, what it is not is emulation or simulation
| Emulation | Emulation is the process of getting a system to work in an environment which it was never designed for. An example of this is that there is a old Atari emulation software that you can download and play old Atari games. In the back ground translations are carried out in order for you to play the games, this has major performance issues. Why emulate, because it is cheaper than to rewrite the entire code. |
| Simulation | Simulation gives you the appearance of a system, as opposed to a system itself. For an example NetApp now have a NetApp simulator that appears and works like actual Netapp hardware but it is not. Another example is a flight simulator it gives the appearance of a real plane but obviously it is not. |
| Virtualization | Virtualization allows you to create virtual environments (Linux , Windows) and to make them appear as if they were the only environment using the physical hardware. A virtual machine will have a BIOS (Phoenix BIOS), NIC's, Storage controller, etc and the virtual machine has no idea that its not the only one using the physical hardware. The ESXi server will intercept the virtual interrupts and redirect to the physical hardware inside the ESX host, this is know as binary translation. |
VMware decide to remove the service console (COS) from its latest kernel (hypervisor), which allows the hypervisor not to have any dependencies on the operating system, which improves reliability and security and the need for many updates (patches). The result is a much more stream-lined O/S (90MB approx) which means that it can be embedded onto a hosts flash drive and thus elimating the need for a local disk drive (more greener environment).
The heart of a ESXi is the VMKernel, this controls the access to the physical hardware, it is similar to other O/S, were processes will be created, file systems are used. The VMkernel is designed for running virtual machines, it focuses on resource scheduling, device drivers, and I/O stacks. You can communicate with the VMkernel via the vSphere API which the vSphere client or vCenter can use.

VMware ESXi server has a number processes that are started, running the ps -Tcjstv command lists over 600 processes running
| vmkeventd | A utility for capturing VMkernel events |
| vpxa | This process is responsible for vCenter Server communications, commands received are passed to the hostd process for processing. |
| vmware-usbarbitrator | VMware USB Arbitration Service, Allows USB devices plugged into the HOST to be usable by the guest. |
| vobd | |
| hostd | The ESXi server host agent, this allows the vSphere client or vCenter access to the host. It consists of two processes hostd-poll |
| net-cdp | CDP is used to share information about other directly-connected Cisco networking equipment, such as upstream physical switches. CDP allows ESX and ESXi administrators to determine which Cisco switch port is connected to a given vSwitch. When CDP is enabled for a particular vSwitch, properties of the Cisco switch, such as device ID, software version, and timeout, may be viewed from the vSphere Client. This information is useful when troubleshooting network connectivity issues related to VLAN tagging methods on virtual and physical port settings. |
| net-lbt | A debugging utility for the new Load-Based Teaming feature |
| busybox (ash) | BusyBox is a software application that provides many standard Unix tools, much like the larger (but more capable) GNU Core Utilities. BusyBox is designed to be a small executable for use with the Linux kernel, which makes it ideal for use with embedded devices. It has been self-dubbed "The Swiss Army Knife of Embedded Linux" Busybox utilities: |
| dcui | Direct Console User Interface (DCUI) process provides a local management console for the ESXi host. |
VMware iSCSI proccess |
|
| vmkiscsid | Vmware Open-iSCSI initiator daemon, see below for the files that are used /etc/vmware/vmkiscsid/iscsid.conf |
| iscsi_trans_vmklink | |
| iscsivmk-log | |
VMware vMotion |
|
| vmotionServer | |
VMware High Availability |
|
| agent | this agent is installed and started when a ESXi server is joined to a HA cluster. |
There are a number of ports that are used by VMware ESXi, here is a list of some of the common ones used
9 |
vCenter server access |
22 |
allows access to ssh |
53 |
used for DNS |
68 (546, 547) |
used for DHCP |
80 (9000) |
vCenter server and vSphere Lifecycle Manager |
161 |
CIM server access |
443 |
This port acts as a reverse proxy to a number of services to allow for Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The vSphere API uses this port for communications. |
902 |
Remote console communication between vSphere client and ESXi host for authentication, migrate and provision |
3260 |
Used Software iSCSI Client |
2233 |
Used for VSAN transport |
5989 |
Allows communication with the CIM broker to obtain hardware health data for the ESXi host |
6999 |
NSX Distributed Logical Router Service |
8000 |
vMotion requests |
8080 |
VSAN used by the Storage Management Service |
8100,8200,8300 |
Used by Fault Tolerance |
8301,8302 |
DVSSync ports are used for synchronizing states of distributed virtual ports between hosts |
12345,23451 |
vSAN Clustering Service |
44046,31031 |
Used for ongoing replication traffic by vSphere Replication and VMware Site Recovery Manager |
ESXi now comes with two powerful command-line utilities vCLI and PowerCLI and also the new Tech Mode Support (TSM) which allows low-level access to the VMkernel so that you can run diagnostic commands.
| vCLI | this is a replacement for the esxcfg commands found in the service console. It is available for both Linux and Windows. |
| PowerCLI | this extends Windows PowerShell to allow for the management of vCenter Server objects, PowerShell is designed to replace the DOS command prompt, it is a powerful scripting tool that can be used to run complex tasks across many ESXi hosts or virtual machines. |
ESXi Server has the below features, although ESXi is free most features will require a license.
- supports 64-bit only
- supports up to 24TB memory per virtual machine
- supports 768 vCPU's per virtual machine
- support for 1GB and 10GB networking
- support for booting from a SAN (providing the network cards)
- supports thin provisioning which is designed to provide a higher level of storage utilization
- support dynamic data growth using available data storage , which includes growing Virtual Machine File Systems (VMFS)
- has it own patch manager to allow for easy patching
- fully supports HA
- supports both virtual machine and storage vMotion
- supports fault tolerance (FT)
- supports distributed resource scheduler (DRS)
- can support a mixed setup including any of the above features
The VMware vNetwork Distributed Switch (dvSwitch) provides centralized configuration of networking for hosts within your vCenter server data center. This means that you can make changes in the vCenter can can then be applied to a number of ESXi hosts or virtual machines. Network I/O control is a new network traffic management feature for dvSwitches it implements a software scheduler within the dvSwitch to isolate and prioritize traffic types on the links that connect your ESXi server to the physical network. It can recognize the following types of traffic
- Virtual Machine
- Management
- iSCSI
- NFS
- Fault Tolerance logging
- vMotion
Network I/O control uses shares and limits to control traffic leaving the dvSwitch, which can be configured on the resource Allocation tab. Limits are imposed before shares and limits apply over a team of NIC's. Shares on the over hand, schedule and prioritize traffic for each physical NIC in a team
- shares - specify the relative importance of a traffic type being transmitted to the hosts physical NICs, shares settings work the same way a CPU and memory resources.
- limits - are used to specify the maximum limit that can be used by a traffic type
VMware also uses Load-Based Teaming (LBT), which is used to avoid network congestion on a ESXi server, it adjusts manually the mapping of virtual ports to physical NIC's to balance network load leaving and entering the dvSwitch. LBT will attempt to move one or more virtual ports to a less utilized link within the dvSwitch.
ESXi can be installed on a flash drive, small local or remote disk drive and as such ESXI differs from other O/S. The system partitions for ESXI are summarized below, this may differ slightly depending if installed on a flash drive or hard disk
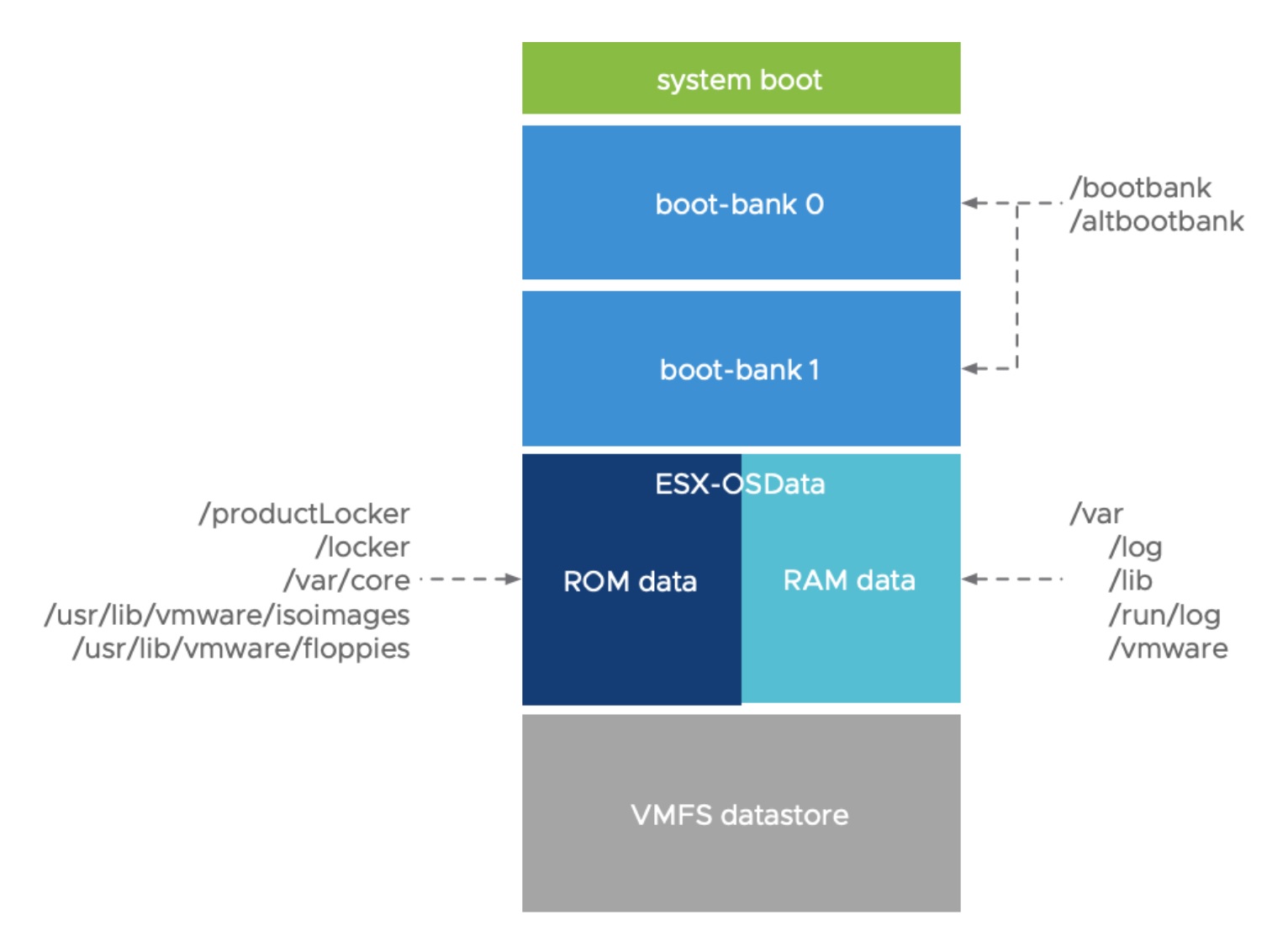
- system boot - Stores boot loader and EFI modules
- boot-bank 0 - System space to store ESXi boot modules
- boot-bank 1 - System space to store ESXi boot modules
- ROM data - Infrequently written data - VMtools ISOs, configurations, and core dumps
- RAM Data - Frequently written data - logs, VMFS global traces, vSAN EPD and traces, and live databases
- VMFS datastore - If the boot media is larger than 128GB, a VMFS datastore is created automatically to use for storing virtual machine data
The sub-systems that require access to the ESXi partitions, access these partitions using the symbolic links. For example: /bootbank and /altbootbank symbolic links are used for accessing the active bootbank and alternative bootbank. The /var/core symbolic link is used to access the core-dumps.
When using secure boot you power on the server the UEFI firmware starts the bootloader (which is digitally signed with the certificate in the the UEFI firmware), the bootloader then validates the digitally signed VMKernel, the VMKernel then runs the VIB verifier (VIB is tar gzipped package digitally signed of the ESXI file system files), ESXI then can reference this package knowing that it is secure.
When your ESXi server first starts, SYSLinux is loaded, SYSLinux looks at the file boot.cfg, SYSLinux uses the parameters build, updated and bootstate to determine which partition to use to boot ESXi.
After SYSlinux determines which system image to boot, boot.cfg is read to determine the files that are used to boot the VMKernel, once loaded into memory the storage is not accessed again. if you run df -h you get a listing of the filesystems that ESXi has mounted includsing any datastores.

The command vdf -h gives details on the RAM disks, some of the mounts are hoststats which is used to store realtime performance data on the host.