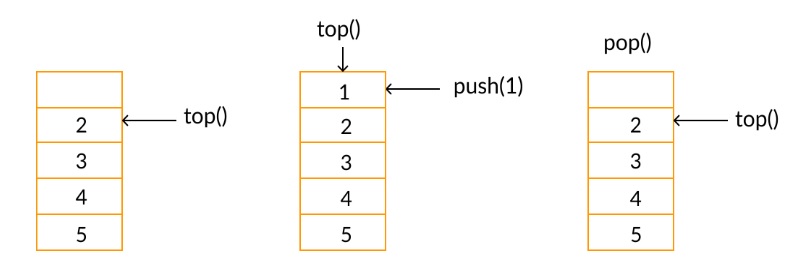
Stacks
Stacks are an abstract data type. the are based on LIFO (Last In First Out), either push onto the top of the stack, pop off of the top of the stack or take a peek at the top of the stack. The data is ordered based on when items were added to the stack.
| Array Stack | package uk.co.datadisk.stack;
import uk.co.datadisk.linkedlist.Employee;
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
public class ArrayStack {
private Employee[] stack;
private int top;
public ArrayStack(int capacity) {
stack = new Employee[capacity];
}
public void push(Employee employee){
if (top == stack.length){
// need to resize the array
Employee[] newArray = new Employee[2 * stack.length];
System.arraycopy(stack, 0, newArray, 0, stack.length);
stack = newArray;
}
stack[top++] = employee;
}
public Employee pop() {
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
Employee employee = stack[--top];
stack[top] = null;
return employee;
}
public Employee peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyStackException();
}
return stack[top -1];
}
public int stackSize(){
return top;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == 0;
}
public void printStack(){
System.out.println();
for (int i = top - 1 ; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.println(stack[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
} |
| Main Array Stack | package uk.co.datadisk.stack;
import uk.co.datadisk.linkedlist.Employee;
public class Main_Stack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee paul = new Employee("Paul", "Valle", 1000);
Employee lorraine = new Employee("Lorraine", "Valle", 1001);
Employee dominic = new Employee("Dominic", "Valle", 1002);
Employee jessica = new Employee("Jessica", "Valle", 1003);
Employee will = new Employee("Will", "Hay", 1004);
Employee graham = new Employee("Graham", "Moffett", 1005);
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(10);
stack.push(paul);
stack.push(lorraine);
stack.push(dominic);
stack.push(jessica);
stack.push(will);
stack.printStack();
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println("Popped: " + stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
stack.push(graham);
System.out.println(stack.peek());
}
} |
The JDK has its own version and you should use the version
| JDK Stack | package uk.co.datadisk.stack;
import uk.co.datadisk.linkedlist.Employee;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class ArrayStack_JDK {
private LinkedList<Employee> stack;
public ArrayStack_JDK() {
this.stack = new LinkedList<>();
}
// We are going only expose pop, push, peek and isEmpty
// You could use synchronize to make it thread safe but there are other options (Deque interface).
public void push(Employee employee){
stack.push(employee);
}
public Employee pop(){
return stack.pop();
}
public Employee peek(){
return stack.peek();
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return stack.isEmpty();
}
public void printStack() {
ListIterator<Employee> iterator = stack.listIterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
} |
| Main JDK Stack | package uk.co.datadisk.stack;
import uk.co.datadisk.linkedlist.Employee;
public class Main_Stack_JDK {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// you can also use a deque which is backed by an array
Employee paul = new Employee("Paul", "Valle", 1000);
Employee lorraine = new Employee("Lorraine", "Valle", 1001);
Employee dominic = new Employee("Dominic", "Valle", 1002);
Employee jessica = new Employee("Jessica", "Valle", 1003);
Employee will = new Employee("Will", "Hay", 1004);
Employee graham = new Employee("Graham", "Moffett", 1005);
ArrayStack_JDK stack= new ArrayStack_JDK();
stack.push(paul);
stack.push(lorraine);
stack.push(dominic);
stack.push(jessica);
stack.printStack();
System.out.println(stack.peek());
System.out.println("Popped: " + stack.pop());
System.out.println(stack.peek());
stack.push(graham);
System.out.println(stack.peek());
}
} |