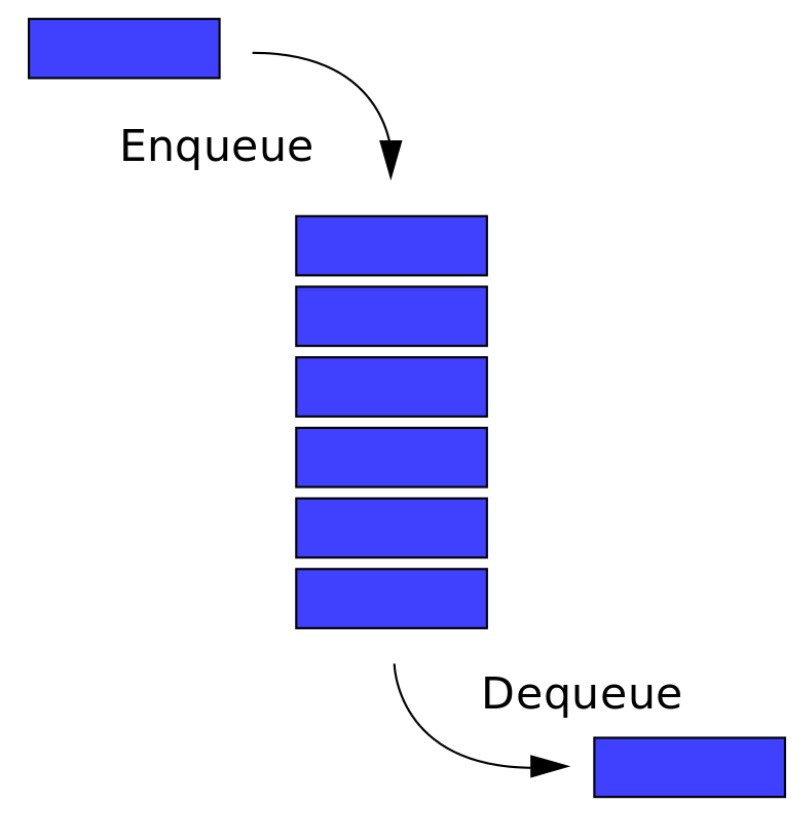
Queues
Queues are an abstract data type. the are based on FIFO (First In First Out), either add onto the end of the queue (enqueue), remove off of the front of the queue (dequeue) or take a peek at the front of the queue. The data is ordered based on when items were added to the queue. You can also implemnet a circular queue, especially you are adding and removing lots of elements
| Array Queue | package uk.co.datadisk.queue;
import uk.co.datadisk.linkedlist.Employee;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
public class ArrayQueue {
private Employee[] queue;
private int front;
private int back; // end of the queue is actually back - 1
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.queue = new Employee[capacity];
}
public void add(Employee employee){
if(back == queue.length){
Employee[] newArray = new Employee[2 * queue.length];
System.arraycopy(queue, 0, newArray, 0, queue.length);
queue = newArray;
}
queue[back++] = employee;
}
public Employee remove(){
if(size() == 0){
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
Employee employee = queue[front];
queue[front] = null;
front++;
if(size() == 0){
front = 0;
back = 0;
}
return employee;
}
public Employee peek(){
if(size() == 0){
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return queue[front];
}
public int size(){
return back - front;
}
public void printQueue() {
for (int i = front; i < back; i++) {
System.out.println(queue[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
} |
| Main Array Queue | package uk.co.datadisk.queue;
import uk.co.datadisk.linkedlist.Employee;
public class Main_Queue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee paul = new Employee("Paul", "Valle", 1000);
Employee lorraine = new Employee("Lorraine", "Valle", 1001);
Employee dominic = new Employee("Dominic", "Valle", 1002);
Employee jessica = new Employee("Jessica", "Valle", 1003);
Employee will = new Employee("Will", "Hay", 1004);
Employee graham = new Employee("Graham", "Moffett", 1005);
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(10);
queue.add(paul);
queue.add(lorraine);
queue.add(dominic);
queue.add(jessica);
queue.printQueue();
System.out.println("Peeked: " + queue.peek());
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
queue.printQueue();
}
} |
| Circular Queue | |
| Array Circular Queue | package uk.co.datadisk.queue;
import uk.co.datadisk.linkedlist.Employee;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
public class ArrayCircularQueue {
private Employee[] queue;
private int front;
private int back; // end of the queue is actually back - 1
public ArrayCircularQueue(int capacity) {
this.queue = new Employee[capacity];
}
public void add(Employee employee){
if(size() == queue.length - 1){
int numItems = size();
Employee[] newArray = new Employee[2 * queue.length];
System.arraycopy(queue, front, newArray, 0, queue.length - front);
System.arraycopy(queue, 0, newArray, queue.length - front, back);
queue = newArray;
front = 0;
back = numItems;
}
queue[back] = employee;
if(back < queue.length -1){
back++;
} else {
back = 0;
}
}
public Employee remove(){
if(size() == 0){
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
Employee employee = queue[front];
queue[front] = null;
front++;
if(size() == 0){
front = 0;
back = 0;
} else if (front == queue.length){
front = 0;
}
return employee;
}
public Employee peek(){
if(size() == 0){
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return queue[front];
}
public int size(){
if(back <= front){
return back - front;
} else {
return (back - front) + queue.length;
}
}
public void printQueue() {
if(back <= front){
for (int i = front; i < back; i++) {
System.out.println(queue[i]);
}
} else {
for (int i = front; i < queue.length; i++) {
System.out.println(queue[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < back; i++) {
System.out.println(queue[i]);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
} |
| Main Array Circular Queue | package uk.co.datadisk.queue;
import uk.co.datadisk.linkedlist.Employee;
public class Main_Circular_Queue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee paul = new Employee("Paul", "Valle", 1000);
Employee lorraine = new Employee("Lorraine", "Valle", 1001);
Employee dominic = new Employee("Dominic", "Valle", 1002);
Employee jessica = new Employee("Jessica", "Valle", 1003);
Employee will = new Employee("Will", "Hay", 1004);
Employee graham = new Employee("Graham", "Moffett", 1005);
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(10);
queue.add(paul);
queue.add(lorraine);
queue.add(dominic);
queue.add(jessica);
queue.add(will);
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
queue.add(graham);
System.out.println("Queue Size: " + queue.size());
queue.printQueue();
System.out.println("Peeked: " + queue.peek());
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
queue.add(paul);
queue.add(lorraine);
queue.add(dominic);
queue.add(jessica);
queue.add(will);
queue.add(paul);
queue.add(lorraine);
queue.add(dominic);
queue.add(jessica);
queue.add(will);
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
queue.remove();
System.out.println("Queue Size: " + queue.size());
queue.printQueue();
}
} |
| Blocking Queue | |
| Blocking Queue example | package uk.co.datadisk;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
class FirstWorker implements Runnable {
private BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue;
public FirstWorker(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
blockingQueue.put("A");
Thread.sleep(1000);
blockingQueue.put("B");
Thread.sleep(1000);
blockingQueue.put("C");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class SecondWorker implements Runnable {
private BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue;
public SecondWorker(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class BlockingQueue1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10);
FirstWorker firstWorker = new FirstWorker(queue);
SecondWorker secondWorker = new SecondWorker(queue);
new Thread(firstWorker).start();
new Thread(secondWorker).start();
}
} |
| Delay Queue | |
| Delay Queue example | package uk.co.datadisk;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
class DelayedWorker implements Delayed {
private long duration;
private String message;
public DelayedWorker(long duration, String message) {
this.duration = System.currentTimeMillis() + duration;
this.message = message;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed otherDelayed) {
if (this.duration < ((DelayedWorker) otherDelayed).getDuration()) {
return -1;
}
if (this.duration > ((DelayedWorker) otherDelayed).getDuration()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit timeUnit) {
return timeUnit.convert(duration - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
public long getDuration() {
return duration;
}
public void setDuration(long duration) {
this.duration = duration;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.message;
}
}
public class DelayQueue1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<DelayedWorker> blockingQueue = new DelayQueue<DelayedWorker>();
try {
blockingQueue.put(new DelayedWorker(1000, "This is message #1"));
blockingQueue.put(new DelayedWorker(10000, "This is message #2"));
blockingQueue.put(new DelayedWorker(4000, "This is message #3"));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
while (!blockingQueue.isEmpty()) {
try {
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} |
| Priority Queue | |
| Priority Queue example | package uk.co.datadisk;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue;
class FirstWorker2 implements Runnable {
private BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue;
public FirstWorker2(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
blockingQueue.put("B");
blockingQueue.put("H");
blockingQueue.put("F");
Thread.sleep(1000);
blockingQueue.put("A");
Thread.sleep(1000);
blockingQueue.put("E");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class SecondWorker2 implements Runnable {
private BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue;
public SecondWorker2(BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue) {
this.blockingQueue = blockingQueue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class PriorityQueue1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> queue = new PriorityBlockingQueue<>();
FirstWorker2 firstWorker = new FirstWorker2(queue);
SecondWorker2 secondWorker = new SecondWorker2(queue);
new Thread(firstWorker).start();
new Thread(secondWorker).start();
}
} |